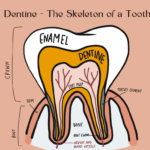
Dentin, also known as dentine, is the skeleton of the tooth as it forms the bulk of the tooth.
Dentin is a calcified tissue stronger than bone but weaker than enamel because of its lesser % by volume of crystalline matrix (calcium and phosphate minerals)
Predominantly, dentine comprises 45-50 % inorganic hydroxyapatite crystals, 25-20% organic material like collagen type-1 fibres and proteins, and the remaining 8-10% is water.
The inorganic component of dentin also finds minerals like Carbonates, which play an essential role in cavity formation.
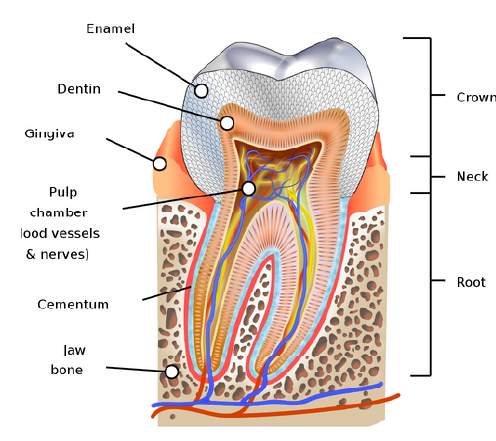
Dentin is technically the second layer, covered outside by the enamel on the crown aspect and Cementum on the roots.
Dentine protects the tooth’s core by enclosing the Dental Pulp within itself from the oral environment and microbes.
This bony porous matrix is yellow, which transmits through the translucent enamel to give the tooth its colour.
The Elastic nature of the dentine supports the enamel and prevents the brittle enamel from fracturing.
Enamel vs Dentine
There are two main distinguishing characteristics between the Enamel and Dentine
1. Dentines continue to form throughout life; they are classified as
- Primary Dentine – first formed dentine- Mantle Dentine and circumpulpal dentine
- Secondary Dentine – They are formed after root completion
- Tertiary Dentine – They are formed in response to external stimuli like decay.
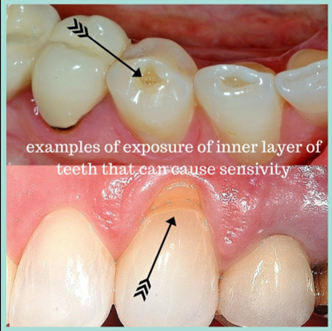
2. Dentine is sensitive to temperature; sometimes, it is hyper-sensitive, mimicking ‘TOOTH PAIN” when exposed due to decay and enamel erosion.
The Channels
What is inside the dentine that makes it respond to hot and cold stimuli?
- Dentinal Tubules – These are the cylindrical channels/hollow tubes which run the entire length of the dentine from the centre pulp of the tooth towards the junction between enamel and dentine in the crown. In the root, it runs till the dentine and cementum junction.
- Size – They are 1-2 µm in diameter. The tubules follow a “s” shaped curvature.
- Contents- It houses the odontoblastic process and dentinal fluid.
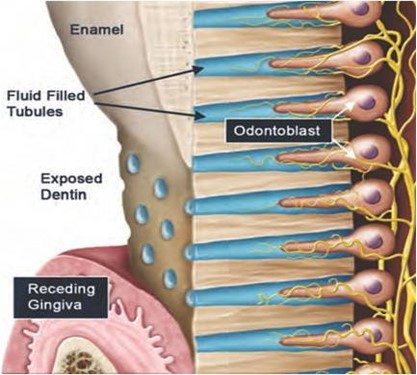
Dentinal Fluid and Dentin Sensitivity
The transudate of plasma from the blood vessels of the pulp forms the Dentinal fluid.
Hydrodynamic Theory
The movement of the dentinal fluid inside the tubule is the main reason behind “Dentin Sensitivity.”
Dentin Sensitivity or Hypersensitivity is described as short, sharp pain responding to a stimulus like “Hot, cold beverages, touch, chemical.
This happens when the dentine gets exposed, damaged by
- Mechanical tooth abrasion due to incorrect/inappropriate tooth brushing
- Gum recession due to gum disease.
- Frequent consumption of acidic and citrus food /beverages
- Teeth grinding habits (parafunctional tooth movements)
- Use of abrasive toothpaste and inferior tooth cleaning products
- Chronic systemic medical conditions lead to gastric issues and frequent vomiting.
The larger surface area of the dentin matrix increases its dissolution when exposed to acids.
This susceptibility is further increased because of the higher carbonate content of the dentin mineral.
Thus, the dentin mineral is dissolved more rapidly than the enamel mineral. Because there is less total mineral in dentin than in enamel, the acid attack proceeds more quickly in dentin. The “S” shaped dentin tubules also provide pathways for this dissolution.
Prevention
The primary and vital preventive protocols for dentin sensitivity are as follows:
- Following proper tooth brushing methods and toothbrush
- Use of safe and recommended fluoridated toothpaste.
- Avoid frequent consumption of aerated and deleterious food substances.
- Conscious correction of parafunctional habits, if required, take the help of a counsellor/habit-breaking appliances like “Splints.”
- Medications to treat chronic ailments for GI complications.
- Dental caries formed should be treated/restored by a dental filling.
- Last but not least, regular biannual dental checkups.
By following the above, dental sensitivity can be controlled. This also prevents one from experiencing sudden, rude, and severe toothache in the middle of the night. I hope this article reassures and restores your beautiful smile.