Tobacco is a plant grown and cultivated in early BC. However, native to America, it has become a ubiquitous name globally, killing millions of people and leaving lakhs of farming households in debt.
Of more than 70 species of Nicotiana plants found, the most common, addictive and harmful ones are Nicotiana Tabacum and Nicotiana Rustica.
The addictive substance found in the Tobacco plant is NICOTINE. It is associated with many health risks and problems.
The tobacco plant leaves, and stems are generally used in commercial preparations.
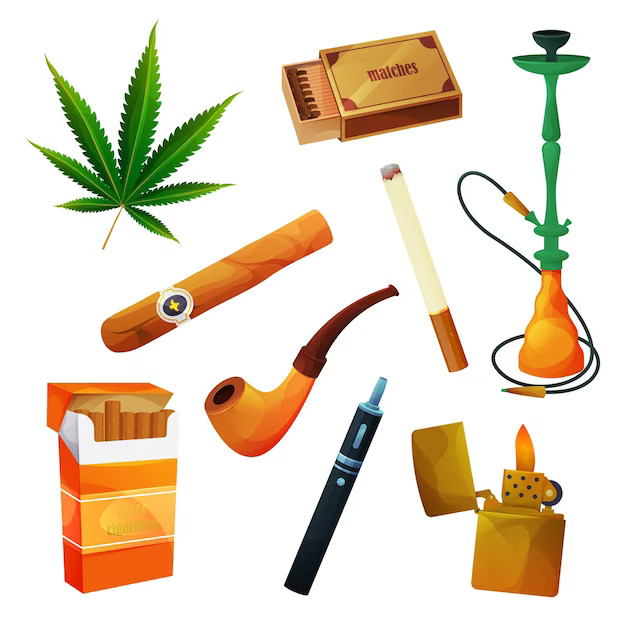
Tobacco is consumed in different ways depending on personal preferences and availability. The common forms of tobacco are:
- Cigarettes
- Cigars
- Pipes
- Water Pipes (Hookahs)
- Smokeless Tobacco. Examples: Snuff, Gutka, Chewing Tobacco, Hans
- Electronic Cigarettes (E-Cigarettes)
E-cigarettes are devices that heat a liquid (e-liquid) that contains nicotine, flavourings, and other chemicals to create an aerosol that the user inhales

Health Hazards
Nicotine in any form affects the Brain, Nervous system, Heart and Blood vessels. Tobacco is connected to cancer of the mouth, throat and lungs.
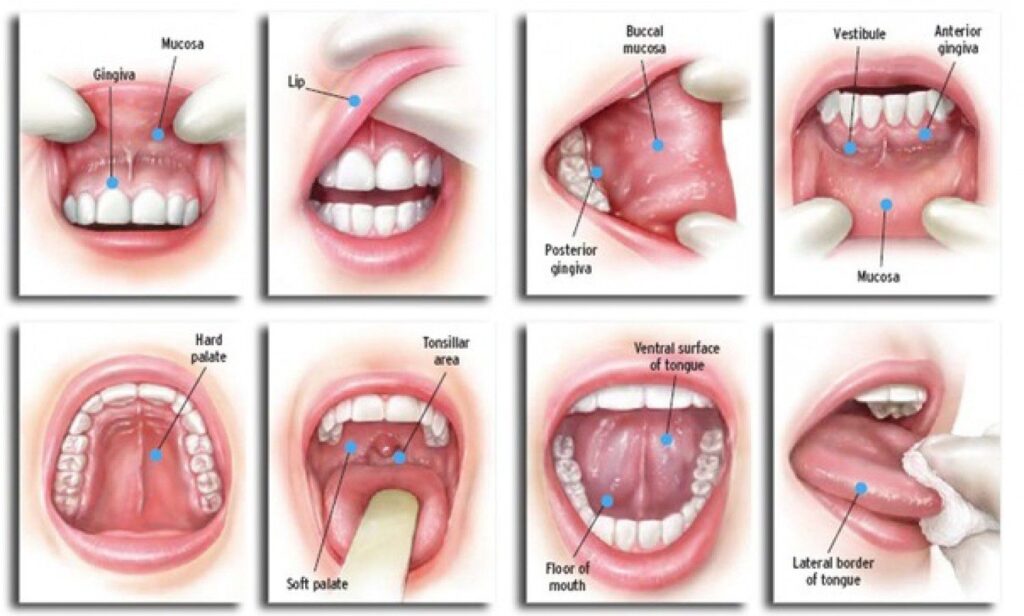
Tobacco and Oral Health
Smoking and smokeless cigarettes have a deleterious effect on the oral cavity’s hard tissue(teeth and bone) and soft tissue (salivary glands, gums, lips, inner lining of oral cavity, tongue, floor of the mouth).
Salivary Glands and Saliva
As the name suggests, salivary glands are a vital part of the oral cavity that helps to secrete saliva.
Saliva is a clear liquid that is 99%water. The key functions of saliva are:
- Helps to keep the mouth moist and comfortable.
- Helps to taste, chew and form the food into a bolus to swallow.
- Helps to protect our teeth from decay and gum disease.
- Salivary Amylase is an enzyme that helps to initiate the first stage of digestion in the mouth.
Smoking can affect the salivary glands and saliva in various ways, such as:
- Reduced salivary production causes dry mouth, which increases the risk of oral infection and dental cavities.
- Increasing the risk of salivary gland tumours.
- Altering the salivary composition leads to impaired salivary protective and lubricating function.
Smoking on Gum Health
Gums/Gingiva are an integral part of Oral tissue that holds the teeth to the underlying jawbone. They are rich in blood supply and nutrients. Smoking can adversely affect the health of the gums. The most common and damaging effects are:
- Smoking reduces the blood flow to gums leading to increased susceptibility to plaque, tartar accumulation and gum infections.
- Gingivitis (gum inflammation) and periodontitis (gum and supporting tissue inflammation) lead to early tooth and bone loss.
- Smoking delays healing, leading to post-extraction complications and infection.
- Smoking causes changes in the cells of the oral tissues, leading to an increased risk of oral cancer.
- Treating the above conditions becomes incredibly challenging for Dentists.
Smokeless Tobacco
Smokeless tobacco is made of tobacco leaves or stems that are chewed, sucked, or pouched in the mouth. Some common forms of smokeless tobacco are snuff, snus, chewing tobacco, gutkha, and betel quid. Smokeless tobacco products contain nicotine and other harmful chemicals that can cause oral cancer, gum disease, tooth decay, and other diseases.

Oral Cancers
One form of Oral cancer is caused due to betel nut chewing / paan chewing. These are pouched in the most convenient part of the mouth for hours together. This form of Tobacco products causes cellular level changes responsible for causing oral cancers. Examples 1. Squamous cell carcinoma, 2. Verrucous cell carcinoma.
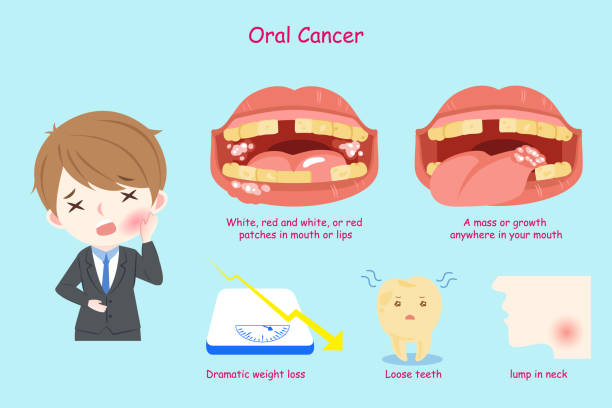
Appearance of the Cancer Lesion
It can affect any part of oral tissue like the cheek, tongue, floor of the mouth, roof of the mouth, and gums.
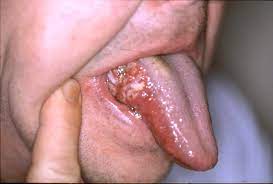
Symptoms
Non-healing recurrent mouth sores (persistent), red / whitish patch on the inner cheek, burning sensation on the cheek and tongue, painful lump on the cheek.
The extent of the lesion can be localised or involve the entire jawbone and underlying lymph nodes too.
Diagnosis
After a thorough intra-oral examination and history taking, a biopsy of the oral lesion is mandatory to confirm the diagnosis.
Treatment
The most sought-after treatment is surgical resection of the lesion, followed by chemotherapy and radiotherapy, depending on the nature and size of the cancer. Besides quitting tobacco, counselling the patient and family members is critical.
Women Smokers

Women/female smokers, besides peer pressure/socialisation, the habit of smoking can be due to low esteem and stress busters.
The common health consequences that women smokers face are the same as their male counterparts, like cancer, heart disease, lung disease, and brain damage.
Besides these, smoking can affect women’s fertility and make it harder to get pregnant.
Smoking by pregnant ladies can have severe consequences for both the mother and the baby. Smoking can also increase the risk of pregnancy complications, such as:
- MISCARRIAGE AND STILLBIRTH – smoking can adversely affect the embryo and cause the unborn child’s death.
- ECTOPIC PREGNANCY – It is a life-threatening condition where the embryo is implanted outside the uterus.
- PRETERM BIRTH – Early labour and babies are delivered prematurely. This causes the babies to develop breathing difficulties and developmental delays.
- LOW BIRTH WEIGHT – Babies born lack low nutritional supply due to decreased blood supply to the placenta, causing low birth weight babies.
- BIRTH DEFECTS – Smoking increases the risk of developing congenital disabilities like cleft lip and palate, affecting the baby’s appearance, feeding, speech and swallowing.
Therefore, smoking by pregnant ladies is very harmful and should be avoided. Quitting smoking is one of the elite ways to protect oneself.
Passive Smokers
Passive smokers are second-hand smokers. They are non-smokers who inhale the smoke from nearby people smoking products like cigarettes, cigars, and pipes.
They can be closest to family members like spouses, children, elders, and other non-smoking people.
It causes serious health hazards like Lung cancers, respiratory infections, and asthma.
It is highly harmful to children, pregnant ladies, and immunocompromised people. WHO (WORLD HEALTH ORGANISATION) survey reveals the death of millions of passive smokers.
Conclusion
Quitting tobacco is one of the things you can do for your health, well-being and your family. There are different ways to quit tobacco. Some of the common ways to quit tobacco are:
- NICOTINE REPLACEMENT THERAPY – Nicotine patches, gums, and tablets containing low nicotine doses help manage withdrawal symptoms. It is readily available over the counter.
- COUNSELING THERAPY.
- YOGA AND MEDITATION.
- DE-ADDICTION CENTRES.
No matter how you choose to quit tobacco, remember that quitting it may take time and effort, but it is worth it for your health and happiness.
On this May 31st World No Tobacco Day, let us all pledge to witness a TOBACCO-FREE WORLD and save lives. Remember to reward yourself for this accomplishment too.